1. Urine Leukocytes Test
Wait 2 Minutes – Expected result: Negative
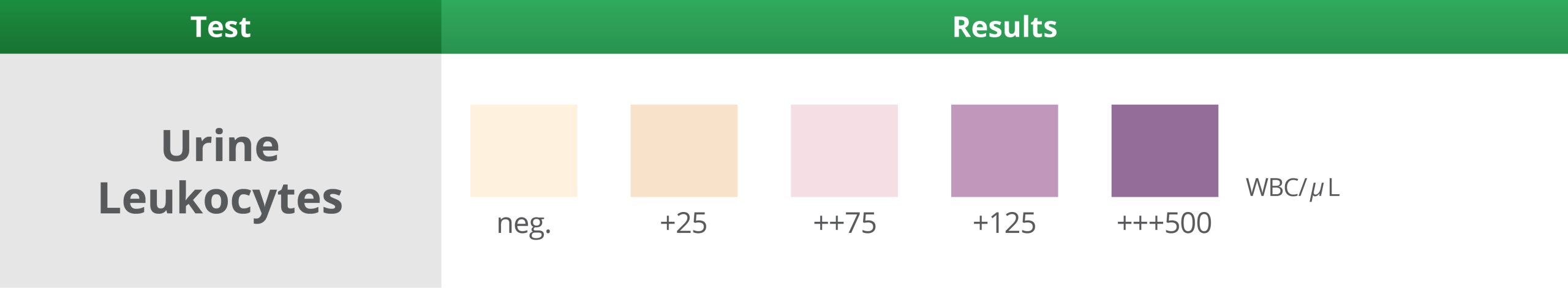
- The detection of white blood cells (WBCs) in the urine may be a sign of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI).
- Kidney stones or a blockage in the urinary tract can also cause more leukocytes to be in your urine.
2. Urine Nitrites Test
Wait 60 Seconds – Expected result: Negative
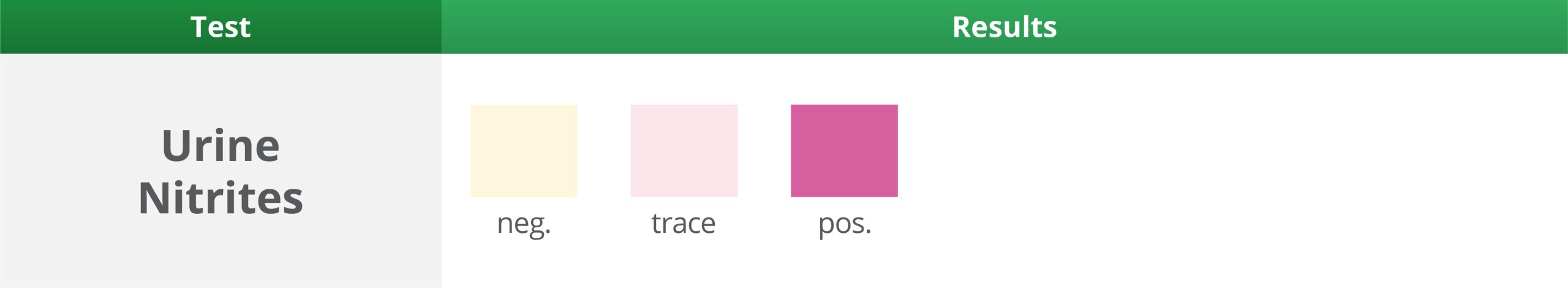
- The presence of nitrites in the urine is suggestive of urinary tract infection.
3. Urine Urobilinogen Test
Wait 60 Seconds – Expected result: less than 1mg/dl)

- It is normal for your urine to contain some urobilinogen. If there is little or no urobilinogen in your urine, it can mean your liver is not working correctly.
- This test is only one measure of your liver function. If your doctor thinks you might have a liver disease, additional urine and blood tests may be ordered.
4. Urine Glucose Test
Wait 30 Seconds – g/dL (%) – Expected result: Negative

- Glucose is not normally in the urine.
- Positive urine glucose test result could indicate diabetes or renal glycosuria and calls for follow-up testing for diabetes.
5. Urine pH level Test
Wait 60 Seconds – Expected result: 5, normal range 4.5 – 8
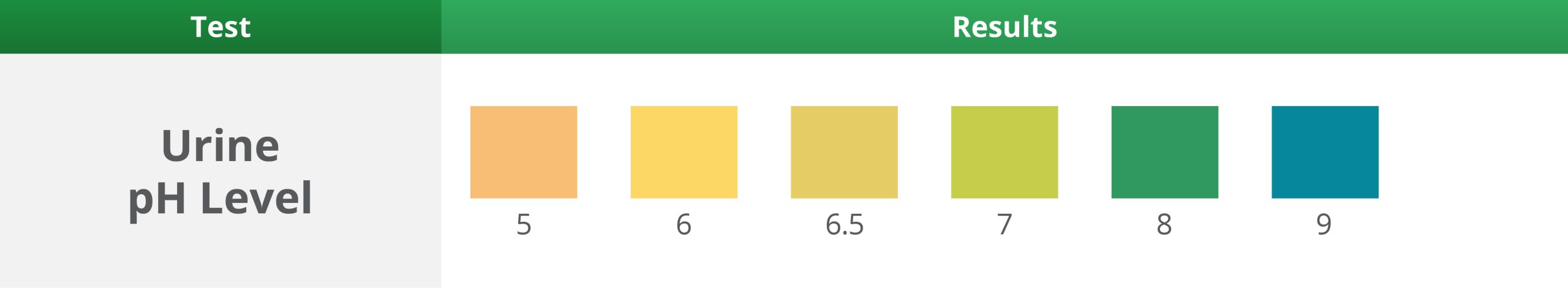
- Causes of low urinary pH include starvation, diabetic ketoacidosis and other conditions that cause metabolic acidosis (e.g. sepsis, high protein diet).
- Causes of high urinary pH include urinary tract infection, conditions that cause metabolic alkalosis (e.g. vomiting) and medications (e.g. diuretics).
6. Urine Specific Gravity Test
Wait 45 Seconds – Expected Results: at 1.000, normal range 1.002 – 1.035
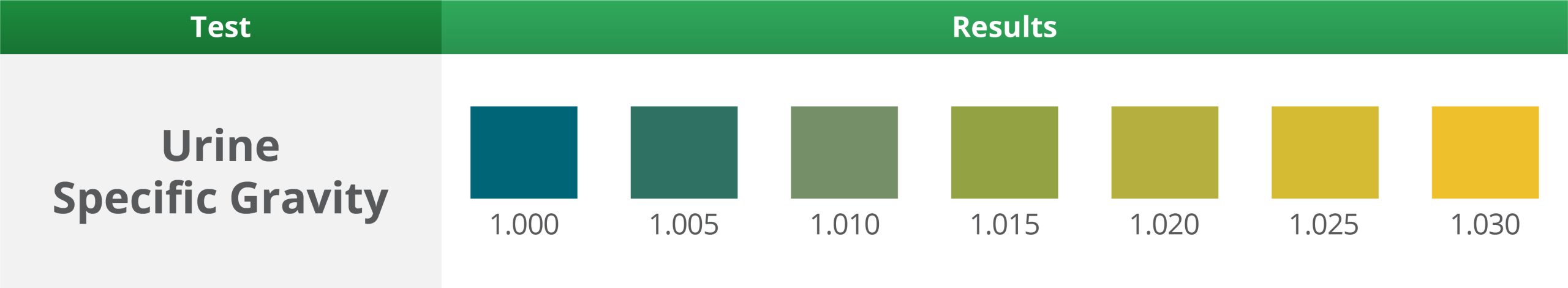
- Causes of low specific gravity include conditions that result in the production of dilute urine, i.e. diabetes insipidus and acute tubular necrosis.
- Causes of high specific gravity include dehydration, glycosuria (e.g. diabetes mellitus) and proteinuria (e.g. nephrotic syndrome).
7. Blood in Urine Test
Wait 60 Seconds – Expected result: Negative
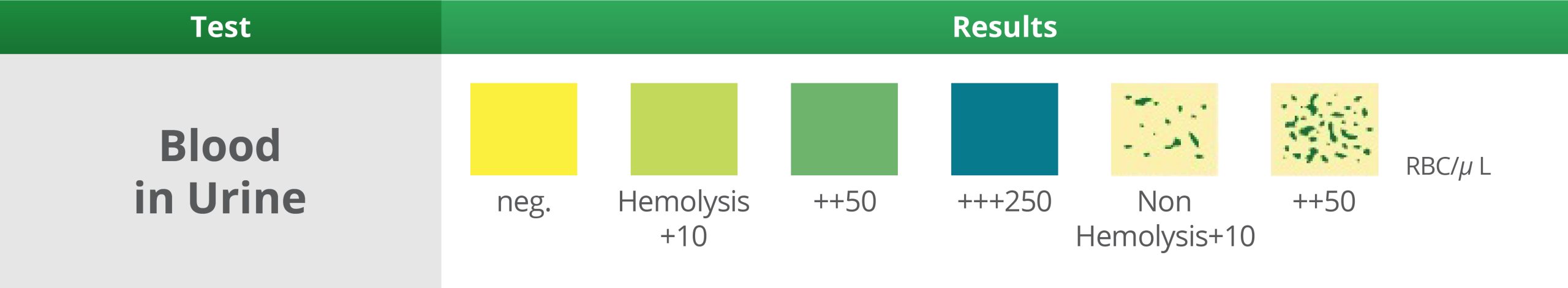
- Blood in the urine may indicate Urinary Tract Infection (UTI), kidney stones, cancers of the urinary tract, nephritic syndrome and/or strenuous exercise.
- False-positive reactions due to menstrual contamination may be seen.
8. Urine Ketone Test
Wait 40 Seconds – Expected result: Negative
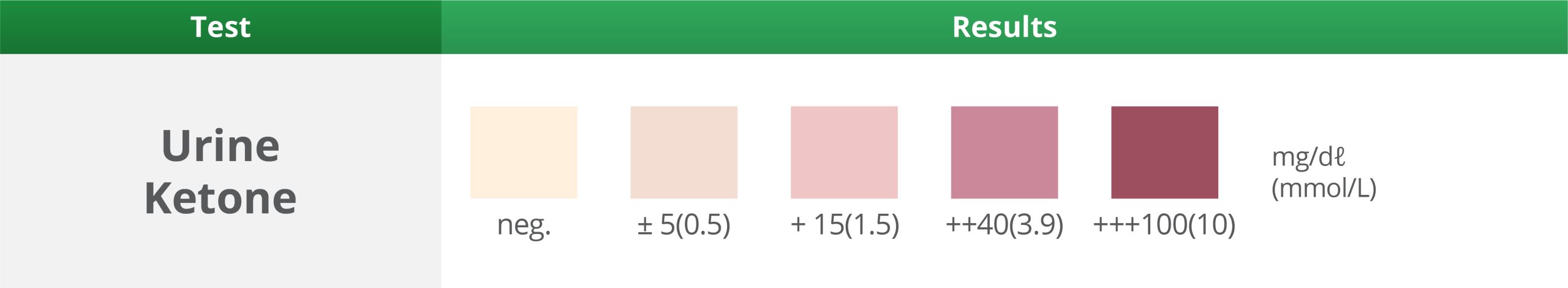
- Measures ketone levels in your urine.
- Presence of ketones in the urine suggests increased fatty acid metabolism, which occurs during starvation and in conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis.
9. Urine Bilirubin Test
Wait 30 Seconds – Expected result: Negative

- The detection of bilirubin in the urine is an early indication of liver disease such as hepatitis, a blockage in the liver drainage system, or a problem with your general liver function.
10. Urine Protein Test
Wait 60 Seconds – Expected result: Negative

- Causes for protein in urine includes nephritic syndrome and chronic kidney disease.
- This test can also be used to monitor kidney status in persons who are already diagnosed with kidney diseases.
Creatinine and Microalbumin
Albumin is a protein used by the body for tissue growth and healing. Albumin can start leaking into the urine if the kidneys are not working properly.
A microalbumin test checks for small amounts of albumin in the urine as an early indicator of kidney disease.
An albumin to creatinine ratio is calculated and is a way to estimate the total daily urine albumin level without having to undergo a full 24-hour urine sample.
Microalbuminuria, an abnormal elevation of the urinary albumin excretion rate, is often one of the first signs of renal disease or damage that can lead to renal failure. Patients with hypertension or diabetes have the highest risk of renal disease where microalbumin may be present.
The results of the microalbumin test (albumin:creatinine ratio) are measured as milligrams (mg) of albumin per gram of creatinine. The results are reported as:
- Less than 30 mg/g is normal
- 30 to 300 mg/g may indicate early kidney disease
- More than 300 mg/g indicates more advanced kidney disease
Which factors may affect Microalbumin test results?
The factors which may affect microalbumin test results are:
- Recent vigorous exercise
- Fever
- Urinary tract infection
- Hematuria
- Certain medications
- Other kidney diseases